- Visibility 341 Views
- Downloads 56 Downloads
- Permissions
- DOI 10.18231/j.ctppc.2024.009
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Synthesis of 2-chloro-benzamides for evaluation antimicrobial and disinfectant activity: Part-I
- Author Details:
-
Sakshi Ghare *
Abstract
2-Chlorobenzamide derivatives have been synthesized and claimed in this research study. The compound SG1 and SG2 were synthesized by known methods Ethylene diamine and isopropyl amine was dissolved in ethanolic 1 N NaOH separately and to it 2-Chlorobenzoyl chloride was added. The products SG1 and SG2 were collected respectively.
Introduction
Benzamide derivatives are known for its versatile medicinal properties.[1] Some of the pharmacological properties of benzamide derivatives include antipsychotic, [2] antihypertensive, [3] antibacterial[4] and antimicrobial [5] properties. The structure of the claimed compounds has been shown in [Figure 1]. The synthesis of benzamides have been reported by many authors.[6]
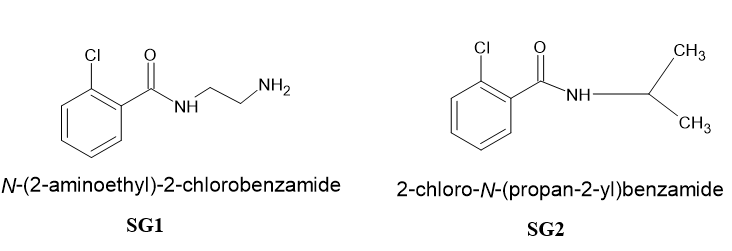
Materials and Methods
TLC was performed on 524nm Merk TLC plates. All chemicals were of synthetic grade and 98% purisis grade. TLC was eluted with 3 different solvents to check the purity of the compounds and visualized in Iodine chamber and further in UV chamber. The 1H-NMR was performed on Bruker 400 MHZ NMR before which FT-IR was performed on Perkin Elmer spectrophotometer. The synthetic scheme for the claimed compounds has been shown in [Figure 2].
Synthetic scheme
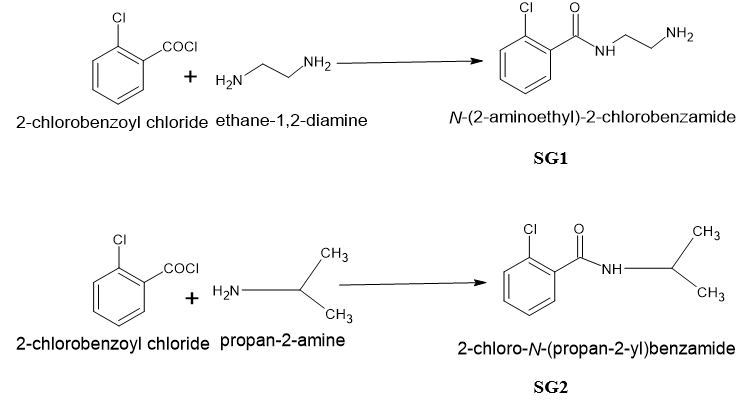
N-(2aminoethyl)-2-chlorobenzamide (SG1): An equimolar solution of ethylene diamine was dissolved in 10 ml of ethanolic 1 N NaOH in round bottom flask and to it 2-Chlorobenzoyl chloride was added dropwise from dropping funnel with continuous stirring for 3 hrs at room temperature. The stirring was conducted on magnetic stirrer with magnetic bead in the ethylene diamine solution. The compound that separated out after 3 hrs was dried. The compound SG1 was washed with ethanol and further dried again washed with NaOH and water and air dried.
FT-IR (λ, cm-1): 3439.6, 3102.9, 3097.8, 3023.5, 2952.4, 1718.8, 1584.8, 1566.3, 1489.0, 1486.2, 1398.6, 1239.6, 1222.2, 1192.9, 1171.1, 929.0, 893.0, 884.5, 1222.2, 1192.9, 11717.1, 929.0, 893.0, 884.5, 786.6, 712.5, 697.0
1HNMR (δ shift in ppm): 2.83 (2H, t, J = 7.2 Hz), 3.47 (2H, t, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.32-7.59 (3H, 7.39 (ddd, J = 8.1, 7.6, 1.4 Hz), 7.51 (ddd, J = 8.4, 7.6, 1.5 Hz), 7.53 (ddd, J = 8.4, 1.4, 0.5 Hz)), 7.90 (1H, ddd, J = 8.1, 1.5, 0.5 Hz)
2-chloro-N-(propan-2-yl) benzamide (SG2): The procedure for the SG1 was repeated and in place of ethylene diamine, isopropyl amine was used. Rest of the procedure remains same.
FT-IR (λ, cm-1): 3459.5, 3436.1, 3384.5, 3114.3, 3098.6, 30882, 3076.0 , 2934.3 , 1743.0, 1584.3, 1570.5, 1551.5, 1448.0, 1450.0, 1492.2, 1149.2, 1072.1, 1023.3, 939.6.
1H-NMR (δ shift in ppm): 1.17 (6H, d, J = 6.8 Hz), 4.20 (1H, sept, J = 6.8 Hz), 7.32-7.59 (3H, 7.39 (ddd, J = 8.1, 7.6, 1.4 Hz), 7.51 (ddd, J = 8.4, 7.6, 1.5 Hz), 7.53 (ddd, J = 8.4, 1.4, 0.5 Hz)), 7.90 (1H, ddd, J = 8.1, 1.5, 0.5 Hz).
Results and Discussion
The compounds complied with IR and NMR spectral data and confirmed to be syhthesized.
Conclusion
From the IR and 1H-NMR data of the compounds, it was confirmed that the compounds were synthesized in Part-I of this paper. Further the evaluation of the compounds shall be done in Part-II of the paper.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- Itoh K, Tomozane H, Hakira H, Sonda S, Asano K, Fujimura M. Synthesis and pharmacological properties of novel benzamide derivatives acting as ligands to the 5-hydroxytryptamine 4 (5-HT4) receptor. . Eur J Med Chem. 1999;34:1101-9. [Google Scholar]
- Reitz A, Baxter E, Codd E, Davis C, Jordan A, Maryanoff B. Orally active benzamide antipsychotic agents with affinity for dopamine D2, serotonin 5-HT1A, and adrenergic α1 receptors. J Med Chem. 1998;41(12):1997-2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii S, Kikuchi E, Watanabe Y, Suzuyama H, Yuasa M, Mori T. Structural development of N-(4-phenoxyphenyl) benzamide derivatives as novel SPAK inhibitors blocking WNK kinase signaling. Bioorganic Med Chem Lett. 2020;30(17). [Google Scholar]
- Stokes N, Baker N, Bennett J, Chauhan P, Collins I, Davies D. Design, synthesis and structure–activity relationships of substituted oxazole–benzamide antibacterial inhibitors of FtsZ.. Bioorganic Med Chem Lett. 2014;24(1):353-62. [Google Scholar]
- Acar C, Yalçın G, Bolelli T, Onurdağ F, Ökten S, Şener F. Synthesis and molecular docking studies of some novel antimicrobial benzamides.. Bioorganic Chem. 2020;94. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinichenko E, Faryna A, Kondrateva V, Vlasova A, Shevchenko V, Melnik A. Synthesis, biological activities and docking studies of novel 4-(arylaminomethyl) benzamide derivatives as potential tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Molecules. 2019;24. [Google Scholar]
How to Cite This Article
Vancouver
Ghare S. Synthesis of 2-chloro-benzamides for evaluation antimicrobial and disinfectant activity: Part-I [Internet]. Curr Trends Pharm Pharm Chem. 2024 [cited 2025 Oct 30];6(1):26-27. Available from: https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ctppc.2024.009
APA
Ghare, S. (2024). Synthesis of 2-chloro-benzamides for evaluation antimicrobial and disinfectant activity: Part-I. Curr Trends Pharm Pharm Chem, 6(1), 26-27. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ctppc.2024.009
MLA
Ghare, Sakshi. "Synthesis of 2-chloro-benzamides for evaluation antimicrobial and disinfectant activity: Part-I." Curr Trends Pharm Pharm Chem, vol. 6, no. 1, 2024, pp. 26-27. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ctppc.2024.009
Chicago
Ghare, S.. "Synthesis of 2-chloro-benzamides for evaluation antimicrobial and disinfectant activity: Part-I." Curr Trends Pharm Pharm Chem 6, no. 1 (2024): 26-27. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ctppc.2024.009
